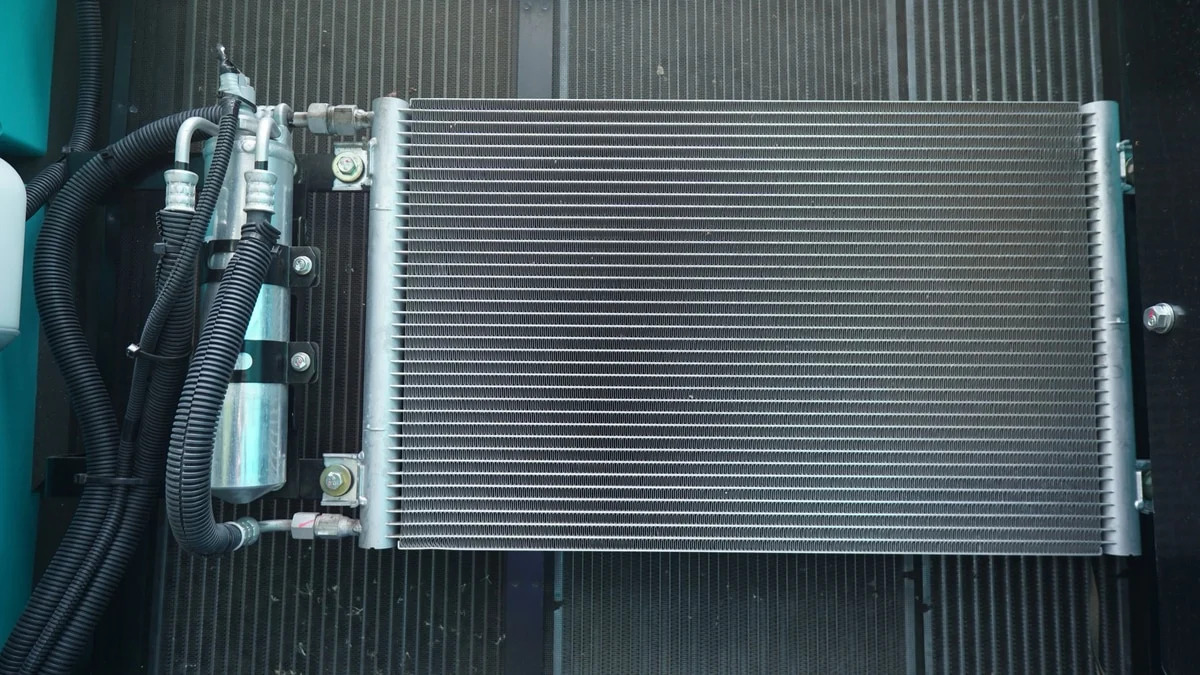
The car condenser is a vital component of the air conditioning system, functioning as a heat exchanger that cools the refrigerant during the condensation process. Positioned in front of the radiator—between the car’s grille and the engine cooling system—the condenser converts high-pressure gas into a high-pressure liquid by releasing heat to the outside air. This process lowers the refrigerant’s temperature, allowing it to circulate efficiently and deliver cool air inside the cabin.
Because of its crucial role, any damage to the condenser can lead to poor A/C performance or complete system failure. This buying guide is designed to help you understand how the condenser works and make an informed decision when choosing the right replacement part for your vehicle.
What is the role of the condenser in an AC system?
The condenser consists of a coil system, radiating fins, an electric fan and tubing connecting it to the compressor and expansion valve.
The condenser is responsible for converting the refrigerant into a liquid and dissipating the heat to the surroundings. Condenser coils are thin tubing that is made up of metal fins, they work to exchange heat away from the Freon or refrigerant gas.
An electric fan blows air over the condenser coils so that it can release heat effectively. The vast surface area of the metal fins is sufficient to expose the refrigerant heat to the outside air and effectively cool it down.